Can an eye doctor detect a brain tumor? This is a question that many people may not think to ask, yet it holds significant importance when it comes to early detection and treatment. Eye doctors, particularly optometrists and ophthalmologists, are often the first line of defense in identifying signs of systemic health issues, including brain tumors. During routine eye exams, they can observe abnormalities in the eyes that may indicate a deeper underlying problem. These abnormalities can serve as early warning signs, prompting further investigation and potentially life-saving interventions.
While eye doctors are not specialists in diagnosing brain tumors, their expertise allows them to identify symptoms that might otherwise go unnoticed. Changes in vision, such as double vision, blurred vision, or loss of peripheral vision, can be linked to pressure or growths in the brain. These symptoms often manifest in the eyes before other physical signs appear, making regular eye exams an essential part of maintaining overall health. Understanding the connection between eye health and brain health can empower individuals to seek timely medical advice and take proactive steps toward diagnosis and treatment.
Eye doctors use advanced tools and techniques to examine the structures of the eye, including the retina and optic nerve. These areas can reveal critical information about the brain’s condition. For instance, swelling of the optic nerve, also known as papilledema, can indicate increased intracranial pressure, which is often associated with brain tumors. By recognizing these signs early, eye doctors can refer patients to neurologists or other specialists for further evaluation. This collaborative approach between eye care professionals and medical specialists underscores the importance of routine eye exams in safeguarding not just vision but overall health.
Read also:Robin Tunney Movies And Tv Shows A Complete Guide To Her Career Highlights
Table of Contents
- Can an Eye Doctor Detect a Brain Tumor?
- How Eye Exams Reveal Brain Tumor Signs?
- What Are the Common Eye Symptoms of Brain Tumors?
- Why Regular Eye Exams Are Critical?
- Can an Eye Doctor Diagnose a Brain Tumor?
- The Role of the Optic Nerve in Brain Tumor Detection
- What Happens After a Suspicious Eye Exam?
- How to Prepare for an Eye Exam?
- When to See a Doctor for Vision Changes?
- Conclusion: The Importance of Early Detection
Can an Eye Doctor Detect a Brain Tumor?
Eye doctors are trained to identify a wide range of conditions, from common refractive errors to more complex systemic diseases. While they cannot directly diagnose brain tumors, they can detect signs that warrant further investigation. During a comprehensive eye exam, an optometrist or ophthalmologist evaluates the health of the eyes, including the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels. These structures can provide clues about the brain's condition. For example, increased intracranial pressure caused by a brain tumor can lead to changes in the optic nerve, which an eye doctor can observe during an exam.
One of the most significant indicators of a potential brain tumor is papilledema, or swelling of the optic nerve. This condition occurs when there is excessive pressure inside the skull, often due to a tumor pressing on the brain. Eye doctors are trained to recognize papilledema and other abnormalities, such as irregularities in the retina or changes in vision. If they detect these signs, they will refer the patient to a neurologist or another specialist for further evaluation. This collaboration between eye care professionals and medical specialists is crucial for early detection and treatment.
It is important to note that not all vision changes are linked to brain tumors. Many eye-related issues, such as cataracts or glaucoma, can cause similar symptoms. However, when combined with other systemic symptoms like headaches, nausea, or seizures, these vision changes may indicate a more serious underlying condition. By understanding the role of eye doctors in detecting brain tumors, patients can take a proactive approach to their health and seek timely medical advice.
How Eye Exams Reveal Brain Tumor Signs?
Eye exams are more than just a routine check for glasses or contact lenses. They involve a detailed examination of the eye's internal structures, which can reveal critical information about the brain's health. During an eye exam, doctors use specialized tools to examine the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels. These structures are closely connected to the brain, making them valuable indicators of neurological conditions.
One of the most common methods used during an eye exam is ophthalmoscopy, which allows the doctor to examine the back of the eye. This procedure can reveal swelling or damage to the optic nerve, which may be caused by increased intracranial pressure. Another technique, called visual field testing, assesses a patient's peripheral vision. Loss of peripheral vision can be a sign of a brain tumor affecting the visual pathways. These tests, combined with a thorough medical history, help eye doctors identify potential issues and recommend further evaluation if necessary.
In addition to these techniques, modern technology has enhanced the ability of eye doctors to detect abnormalities. Advanced imaging tools, such as optical coherence tomography (OCT), provide detailed cross-sectional images of the retina and optic nerve. These images can reveal subtle changes that may not be visible during a standard exam. By leveraging these tools, eye doctors can play a crucial role in the early detection of brain tumors and other serious conditions.
Read also:Unveiling The Mystery Of The Tractor Supply Giant Chicken Skeleton A Fascinating Deep Dive
What Are the Common Eye Symptoms of Brain Tumors?
Brain tumors can cause a variety of symptoms that manifest in the eyes. These symptoms often occur because the tumor affects the brain's ability to process visual information or because it increases pressure on the optic nerve. Recognizing these symptoms can help patients seek timely medical attention and improve their chances of successful treatment. Here are some of the most common eye-related symptoms associated with brain tumors:
- Double Vision: Also known as diplopia, double vision occurs when the eyes are unable to align properly. This can happen if a brain tumor affects the cranial nerves responsible for eye movement.
- Blurred Vision: Blurred vision may result from pressure on the optic nerve or damage to the visual pathways in the brain.
- Loss of Peripheral Vision: A brain tumor can compress the visual pathways, leading to a loss of peripheral vision in one or both eyes.
- Eye Pain: In some cases, patients may experience pain or discomfort in or around the eyes, especially when moving them.
- Swelling of the Optic Nerve: Papilledema, or swelling of the optic nerve, is a key indicator of increased intracranial pressure, which can be caused by a brain tumor.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult an eye doctor or medical professional promptly. While these symptoms do not necessarily indicate a brain tumor, they may signal other serious conditions that require attention.
Why Regular Eye Exams Are Critical?
Regular eye exams are not just about maintaining good vision; they are an essential component of overall health care. Eye doctors are often the first to detect signs of systemic diseases, including diabetes, hypertension, and even brain tumors. By scheduling routine eye exams, patients can ensure that any potential issues are identified early, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
During a comprehensive eye exam, doctors evaluate not only the clarity of vision but also the health of the eye's internal structures. This includes examining the retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels, all of which can provide valuable insights into the brain's condition. For example, changes in the optic nerve or retina may indicate increased intracranial pressure, a common symptom of brain tumors. By catching these signs early, eye doctors can refer patients to specialists for further evaluation, potentially saving lives.
Moreover, regular eye exams can help detect vision changes that may go unnoticed in daily life. Many people adapt to gradual changes in their vision, such as blurred or double vision, without realizing the underlying cause. By addressing these changes early, patients can prevent further complications and improve their quality of life. In the context of brain tumors, early detection can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes and overall prognosis.
Can an Eye Doctor Diagnose a Brain Tumor?
While eye doctors are skilled at identifying signs of brain tumors, they cannot diagnose these conditions on their own. Their role is to recognize abnormalities during an eye exam and refer patients to specialists for further evaluation. For example, if an eye doctor detects swelling of the optic nerve or other concerning symptoms, they will recommend that the patient see a neurologist or oncologist for diagnostic imaging and testing.
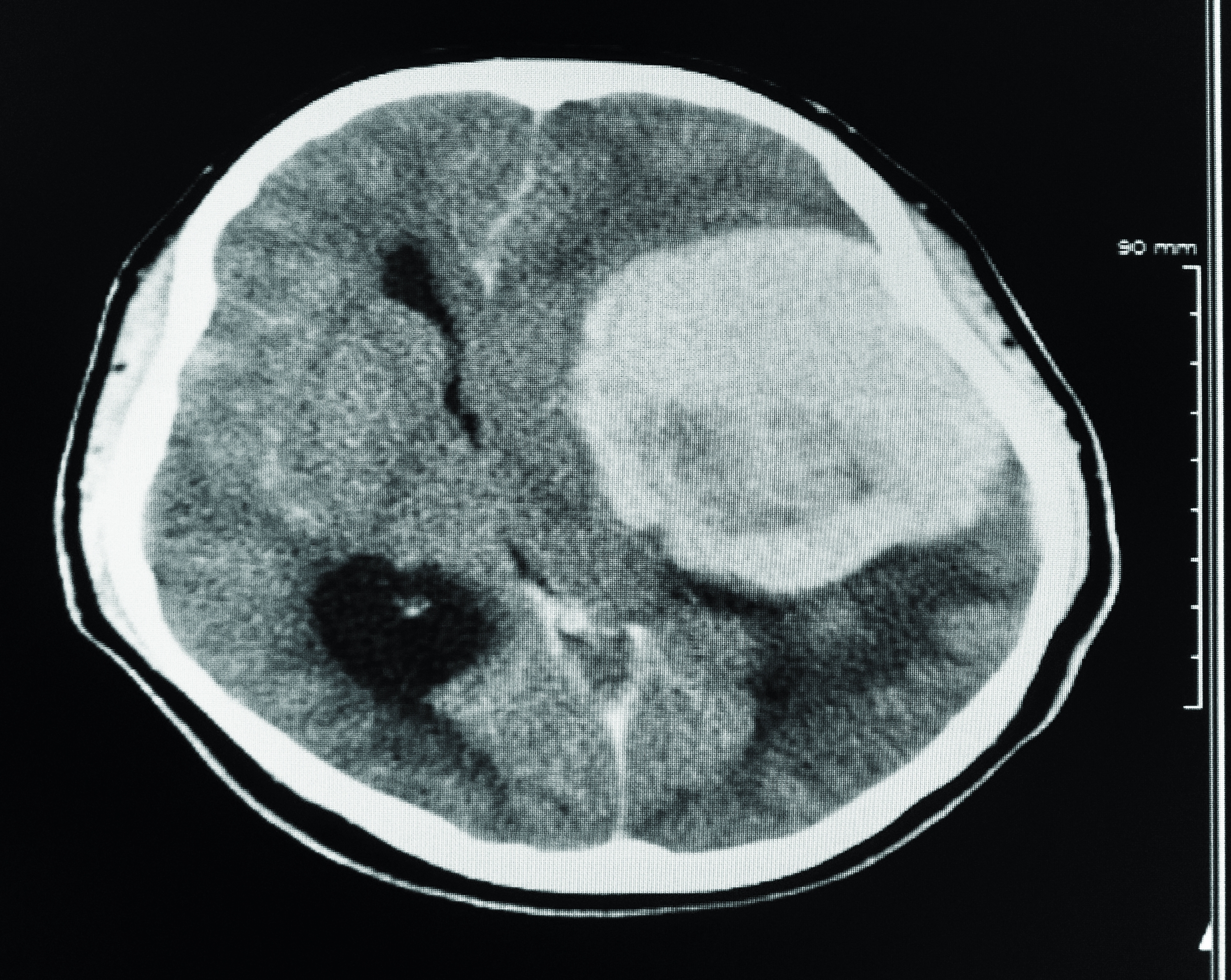
Diagnostic tools such as MRI or CT scans are typically used to confirm the presence of a brain tumor. These imaging techniques provide detailed pictures of the brain, allowing specialists to identify the location, size, and type of tumor. While eye doctors cannot perform these tests, their observations during an eye exam can serve as a crucial first step in the diagnostic process. This collaboration between eye care professionals and medical specialists highlights the importance of a multidisciplinary approach to health care.
It is also worth noting that not all vision changes detected during an eye exam are related to brain tumors. Many eye-related conditions, such as cataracts, glaucoma, or macular degeneration, can cause similar symptoms. However, when combined with other systemic symptoms like headaches, nausea, or seizures, these vision changes may indicate a more serious underlying condition. By working closely with other medical professionals, eye doctors can ensure that patients receive the care they need.
The Role of the Optic Nerve in Brain Tumor Detection
The optic nerve plays a critical role in the detection of brain tumors. This nerve connects the eye to the brain, transmitting visual information for processing. Because of its close connection to the brain, the optic nerve is highly sensitive to changes in intracranial pressure. When a brain tumor causes increased pressure inside the skull, it can compress or damage the optic nerve, leading to visible changes during an eye exam.
One of the most common signs of increased intracranial pressure is papilledema, or swelling of the optic nerve. This condition can be detected during a routine eye exam using ophthalmoscopy, a procedure that allows the doctor to examine the back of the eye. Papilledema is a red flag for potential brain tumors and requires immediate further evaluation. In some cases, the optic nerve may also show signs of atrophy, or shrinkage, which can occur if the nerve has been damaged over time.
By monitoring the health of the optic nerve, eye doctors can identify early warning signs of brain tumors and other neurological conditions. This underscores the importance of regular eye exams, as they provide an opportunity to detect these changes before they lead to more severe symptoms. Early detection can significantly improve treatment outcomes and quality of life for patients.
What Happens After a Suspicious Eye Exam?
If an eye doctor identifies signs that may indicate a brain tumor during an eye exam, the next step is to refer the patient to a specialist for further evaluation. This typically involves a neurologist or oncologist, who will conduct additional tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include imaging studies such as MRI or CT scans, which provide detailed pictures of the brain and help identify the location and size of the tumor.
During this process, patients may also undergo a neurological examination to assess their overall brain function. This exam evaluates factors such as vision, balance, coordination, and reflexes. If the imaging studies confirm the presence of a brain tumor, the specialist will develop a treatment plan based on the type, size, and location of the tumor. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or a combination of these approaches.
Throughout this process, communication between the eye doctor and the specialist is essential. The eye doctor's observations during the initial exam provide valuable information that can guide the diagnostic process. By working together, these professionals can ensure that patients receive the care they need in a timely and effective manner.
How to Prepare for an Eye Exam?
Preparing for an eye exam can help ensure that the results are as accurate