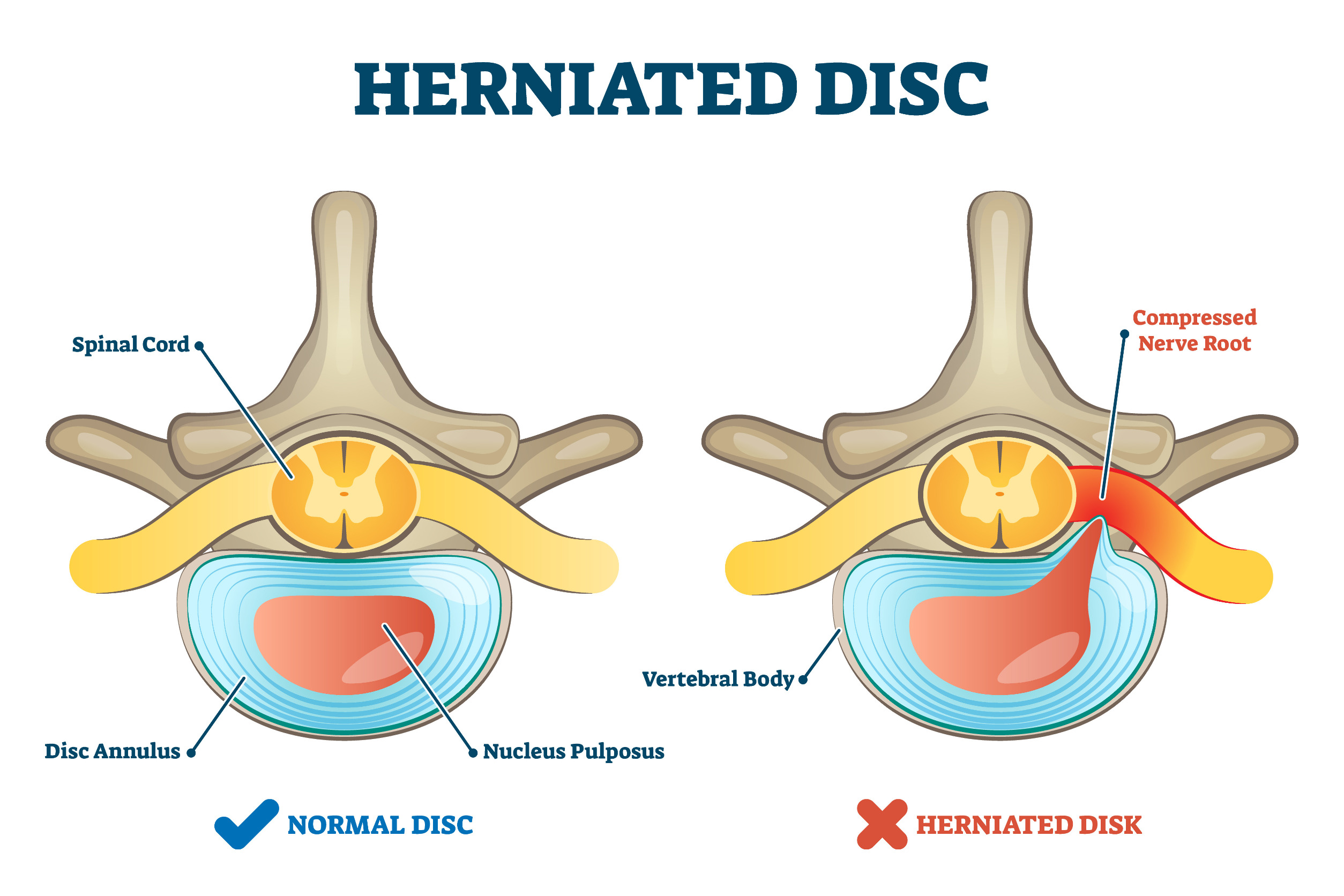
Living with back pain can significantly impact your daily life, and two common culprits behind this discomfort are herniated discs and facet arthropathy. These conditions, though distinct, often coexist and can lead to chronic pain, reduced mobility, and a diminished quality of life. A herniated disc occurs when the soft, gel-like center of a spinal disc pushes through a crack in the tougher exterior, irritating nearby nerves. Facet arthropathy, on the other hand, involves the degeneration of the small joints in the spine, leading to stiffness and localized pain. Understanding these conditions is the first step toward finding relief and regaining control over your life.
Both herniated disc and facet arthropathy are prevalent among adults, especially those over the age of 40. Factors such as aging, poor posture, repetitive strain, and injuries contribute to their development. While herniated discs often cause radiating pain, numbness, or weakness in the limbs, facet arthropathy tends to result in localized pain that worsens with movement. Despite their differences, these conditions share common risk factors and may require similar approaches to treatment, including physical therapy, lifestyle adjustments, and, in severe cases, surgery.
Whether you're seeking answers for yourself or a loved one, this article dives deep into the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for herniated disc and facet arthropathy. By exploring the latest medical insights and expert advice, we aim to provide you with actionable information to help you manage your condition effectively. Keep reading to discover how you can take the first steps toward a pain-free life.
Read also:Unpacking The Intricacies Of Georgie And Mandys First Marriage A Comprehensive Analysis
Table of Contents
- What Causes Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy?
- How Do You Know If You Have a Herniated Disc or Facet Arthropathy?
- Can Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy Be Treated Without Surgery?
- What Are the Best Exercises for Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy?
- How Does Aging Affect Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy?
- Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy
- The Role of Physical Therapy in Treating Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy
- Surgical Options for Severe Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy
- Alternative Treatments for Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy
- Frequently Asked Questions About Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy
What Causes Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy?
Understanding the root causes of herniated disc and facet arthropathy is essential for prevention and effective treatment. A herniated disc typically occurs when the outer layer of a spinal disc weakens, often due to aging, repetitive strain, or sudden trauma. This weakening allows the inner material to bulge outward, potentially pressing on nearby nerves and causing pain. Facet arthropathy, on the other hand, is primarily caused by the wear and tear of the facet joints in the spine, which are responsible for enabling smooth movement between vertebrae.
Several factors can increase your risk of developing these conditions. Poor posture, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle are common contributors to both herniated disc and facet arthropathy. Additionally, occupations that involve heavy lifting or repetitive bending can accelerate spinal degeneration. Genetics also play a role, as some individuals are predisposed to weaker spinal structures. By addressing these risk factors, you can reduce your chances of experiencing the debilitating symptoms associated with these conditions.
How Do You Know If You Have a Herniated Disc or Facet Arthropathy?
Identifying whether you have a herniated disc or facet arthropathy can be challenging, as their symptoms often overlap. However, there are key differences that can help you and your healthcare provider make an accurate diagnosis. Herniated disc symptoms often include sharp, radiating pain that travels down the arms or legs, numbness, tingling, or muscle weakness. These symptoms occur because the herniated disc presses on nearby nerves, disrupting their normal function.
In contrast, facet arthropathy tends to cause localized pain in the neck or lower back, which worsens with movement or prolonged periods of inactivity. Stiffness and reduced range of motion are also common signs of this condition. Diagnostic tools such as MRI scans, X-rays, and physical examinations are often used to differentiate between the two. If you're experiencing persistent back pain, it's crucial to consult a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Can Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy Be Treated Without Surgery?
Many individuals with herniated disc and facet arthropathy find relief through non-surgical treatments. These approaches focus on reducing pain, improving mobility, and addressing the underlying causes of the conditions. Physical therapy is one of the most effective non-surgical treatments, as it strengthens the muscles supporting the spine and improves flexibility. Techniques such as stretching, core strengthening exercises, and posture correction can significantly alleviate symptoms.
Other non-surgical options include medications like anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, and muscle relaxants. In some cases, epidural steroid injections may be recommended to reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief. Lifestyle modifications, such as weight management, ergonomic adjustments, and avoiding activities that strain the spine, can also play a crucial role in managing these conditions. While surgery is sometimes necessary for severe cases, many patients achieve significant improvement through conservative treatments.
Read also:Juan Pablo Di Pace The Versatile Star Who Captivates Audiences Worldwide
What Are the Best Exercises for Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy?
Exercise is a cornerstone of managing herniated disc and facet arthropathy, as it helps strengthen the muscles around the spine, improve flexibility, and reduce pain. Low-impact activities such as swimming, walking, and yoga are particularly beneficial, as they minimize stress on the spine while promoting overall fitness. Core-strengthening exercises, like planks and pelvic tilts, are also highly effective in providing additional support to the spine.
It's important to avoid high-impact exercises or activities that involve heavy lifting, twisting, or sudden movements, as these can exacerbate symptoms. Instead, focus on controlled, gentle movements that gradually increase in intensity. Working with a physical therapist can help you design a personalized exercise program tailored to your specific needs and limitations. By incorporating these exercises into your routine, you can enhance your recovery and prevent future flare-ups.
How Does Aging Affect Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy?
Aging is one of the most significant risk factors for both herniated disc and facet arthropathy. As we grow older, the discs in our spine lose water content, making them less flexible and more prone to damage. This natural degeneration increases the likelihood of disc herniation, especially in individuals with a history of back problems. Similarly, the facet joints in the spine undergo wear and tear over time, leading to the development of facet arthropathy.
While aging is inevitable, there are steps you can take to slow down the progression of these conditions. Maintaining a healthy weight, staying physically active, and practicing good posture can all help protect your spine as you age. Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider can also help detect early signs of spinal degeneration, allowing for timely intervention and treatment.
Lifestyle Changes to Prevent Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy
Making certain lifestyle changes can significantly reduce your risk of developing herniated disc and facet arthropathy. One of the most effective strategies is maintaining a healthy weight, as excess body weight places additional strain on the spine. Incorporating a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids, can also support spinal health.
Additionally, adopting proper ergonomics in your daily activities can prevent unnecessary strain on your back. This includes using supportive chairs, practicing good posture, and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing. Regular physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can further strengthen your spine and improve overall mobility. By taking these proactive steps, you can protect your spine and reduce the likelihood of developing these painful conditions.
The Role of Physical Therapy in Treating Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy
Physical therapy plays a vital role in the management and treatment of herniated disc and facet arthropathy. A skilled physical therapist can design a customized program that addresses your specific symptoms and limitations. This may include a combination of manual therapy, stretching, strengthening exercises, and posture correction techniques.
Manual therapy, such as massage and joint mobilization, can help reduce pain and improve mobility. Stretching exercises target tight muscles and improve flexibility, while strengthening exercises focus on building the muscles that support the spine. Posture correction is also essential, as poor posture can exacerbate symptoms and lead to further degeneration. By working closely with a physical therapist, you can achieve long-term relief and improve your quality of life.
Surgical Options for Severe Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy
In cases where non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief, surgery may be considered for herniated disc and facet arthropathy. Common surgical procedures for herniated discs include discectomy, which involves removing the portion of the disc pressing on a nerve, and spinal fusion, which stabilizes the spine by joining two or more vertebrae. For facet arthropathy, procedures such as facet joint injections or radiofrequency ablation may be used to alleviate pain.
While surgery can be highly effective, it is typically reserved for severe cases where conservative treatments have been exhausted. It's important to discuss the risks and benefits of surgery with your healthcare provider to determine if it's the right option for you. Post-surgical rehabilitation, including physical therapy, is often necessary to ensure a successful recovery.
Alternative Treatments for Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy
For those seeking alternative approaches to managing herniated disc and facet arthropathy, several complementary therapies may provide relief. Acupuncture, for example, has been shown to reduce pain and improve function in individuals with chronic back pain. Chiropractic care, when performed by a licensed professional, can also help realign the spine and alleviate pressure on nerves.
Other alternative treatments include mindfulness-based stress reduction, yoga, and herbal supplements. While these therapies may not cure herniated disc and facet arthropathy, they can complement traditional treatments and improve overall well-being. It's important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any alternative treatment to ensure its safety and effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions About Herniated Disc and Facet Arthropathy
Below are some common questions and answers about herniated disc and facet arthropathy:
- What is the difference between a herniated disc and facet arthropathy? A herniated disc involves the displacement of disc material, while facet arthropathy refers to the degeneration of spinal joints.
- Can herniated disc and facet arthropathy be cured? While these conditions cannot always be cured, they can often be managed effectively with treatment.
- How long does it take to recover from herniated disc and facet arthropathy? Recovery time varies depending on the severity of the condition and the treatment approach.
By addressing these frequently asked questions, we
_1682489757.jpg)