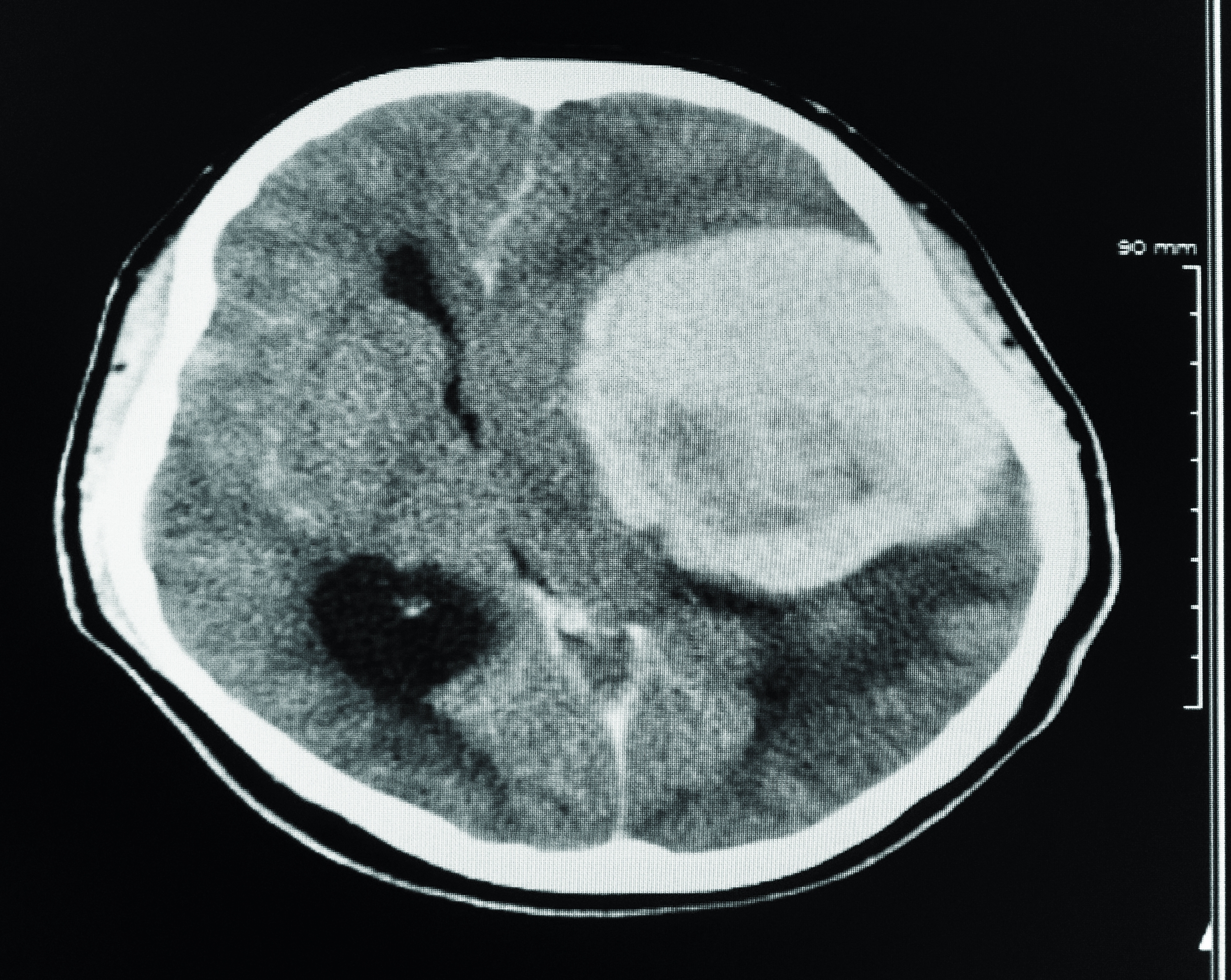
Many people are unaware that routine eye exams can sometimes reveal more than just vision problems. In some cases, an eye exam may uncover signs of a serious underlying health condition, such as a brain tumor. This surprising link between eye health and brain health has sparked curiosity among patients and healthcare professionals alike. While an eye exam is not a direct diagnostic tool for brain tumors, certain symptoms detected during the examination can prompt further investigation into potential neurological issues. Eye doctors, or optometrists, are trained to identify abnormalities in the eyes that may indicate systemic health concerns. This makes regular eye exams an essential part of maintaining overall well-being.
During an eye exam, the optometrist examines various aspects of eye health, including the optic nerve, retina, and blood vessels. These structures can sometimes show signs of pressure or damage caused by a brain tumor. For instance, swelling of the optic nerve, also known as papilledema, can indicate increased intracranial pressure—a potential warning sign of a brain tumor. Although not all cases of papilledema are linked to tumors, its presence warrants immediate medical attention to rule out serious conditions.
While the idea that an eye exam can detect a brain tumor may sound alarming, it highlights the importance of regular check-ups. Early detection of potential issues can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment, improving outcomes for patients. In this article, we will explore the connection between eye exams and brain tumors, answer common questions, and provide valuable insights to help you better understand this fascinating aspect of healthcare. Let’s dive deeper into how an eye exam might just save your life.
Read also:Unveiling The Life Of Rob Dyrdeks Wife A Deep Dive Into Their Beautiful Journey Together
- Can an Eye Exam Detect a Brain Tumor?
- How Does an Eye Exam Reveal Signs of a Brain Tumor?
- What Are the Warning Signs to Watch For?
- Can an Eye Exam Detect Other Health Conditions?
- What Happens After a Suspicious Eye Exam?
- Is a Brain Tumor the Only Cause of Optic Nerve Swelling?
- Why Are Regular Eye Exams Important for Overall Health?
- How Can You Prepare for an Eye Exam?
- What Should You Do If a Brain Tumor Is Suspected?
- Conclusion: Can an Eye Exam Detect a Brain Tumor?
Can an Eye Exam Detect a Brain Tumor?
While an eye exam is primarily designed to assess vision and eye health, it can sometimes uncover signs of a brain tumor. This is because the eyes are closely connected to the brain through the optic nerve, which serves as a direct pathway for visual information. Any disruption or pressure on the optic nerve can manifest as visible changes during an eye exam. For example, swelling of the optic nerve, known as papilledema, can indicate increased intracranial pressure, which may be caused by a brain tumor.
It’s important to note that an eye exam alone cannot diagnose a brain tumor. However, it can serve as an early warning system, prompting further investigation by a neurologist or other specialist. If your optometrist notices abnormalities during your eye exam, they may refer you for imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, to determine the underlying cause. This collaborative approach between eye care professionals and medical specialists highlights the importance of comprehensive healthcare.
How Does an Eye Exam Reveal Signs of a Brain Tumor?
An eye exam involves a series of tests to evaluate the health of your eyes and your vision. During these tests, the optometrist examines the back of the eye, including the retina and optic nerve. If a brain tumor is present, it can cause increased pressure inside the skull, which may lead to swelling of the optic nerve. This swelling, known as papilledema, is often one of the first signs that something is wrong.
In addition to papilledema, other symptoms that may be detected during an eye exam include vision changes, double vision, or loss of peripheral vision. These symptoms can occur if the tumor is pressing on the optic nerve or other parts of the brain responsible for vision. While these signs do not necessarily mean a brain tumor is present, they should not be ignored. Early detection and treatment are crucial for improving outcomes in cases where a tumor is diagnosed.
What Are the Warning Signs to Watch For?
If you’re wondering whether an eye exam can detect a brain tumor, it’s helpful to know the warning signs that might prompt further investigation. Some of the most common symptoms include:
- Sudden or gradual vision loss
- Double vision or blurred vision
- Headaches accompanied by vision changes
- Loss of peripheral vision
- Swelling or discoloration of the optic nerve
These symptoms can vary depending on the size, location, and type of brain tumor. In some cases, patients may not experience any noticeable symptoms until the tumor has grown significantly. This is why regular eye exams are so important, as they can help identify potential issues before they become severe.
Read also:Discover The Stars Of 911 Lone Star Everything You Need To Know About The Cast
Can an Eye Exam Detect Other Health Conditions?
While the focus of this article is on whether an eye exam can detect a brain tumor, it’s worth noting that eye exams can reveal a wide range of other health conditions. The eyes are often referred to as a “window to the body” because they can provide insights into systemic health. For example, an eye exam may detect signs of diabetes, high blood pressure, or even autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis.
Optometrists are trained to recognize abnormalities that may indicate underlying health issues. By examining the blood vessels, retina, and optic nerve, they can identify changes that may require further medical evaluation. This makes regular eye exams an essential component of preventive healthcare, as they can help detect conditions before they cause noticeable symptoms.
What Happens After a Suspicious Eye Exam?
If your optometrist detects abnormalities during your eye exam that suggest a potential brain tumor, they will likely refer you to a neurologist or other specialist for further evaluation. The next steps typically involve imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, to get a clearer picture of what’s happening inside your brain. These tests can help determine whether a tumor is present and, if so, its size, location, and type.
It’s important to stay calm and proactive during this process. While the possibility of a brain tumor can be frightening, early detection and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. Your healthcare team will work with you to develop a plan that addresses your specific needs and ensures the best possible care.
Is a Brain Tumor the Only Cause of Optic Nerve Swelling?
While a brain tumor is one possible cause of optic nerve swelling, it is not the only one. Other conditions, such as idiopathic intracranial hypertension (IIH), infections, or inflammatory diseases, can also lead to papilledema. IIH, for example, is a condition characterized by increased intracranial pressure without an identifiable cause. It is more common in young, overweight women and can mimic the symptoms of a brain tumor.
To determine the underlying cause of optic nerve swelling, your healthcare provider will consider your medical history, symptoms, and the results of diagnostic tests. This comprehensive approach ensures an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. If you’re concerned about whether an eye exam can detect a brain tumor, rest assured that your optometrist will take all necessary steps to investigate any abnormalities they find.
Why Are Regular Eye Exams Important for Overall Health?
Regular eye exams are about more than just checking your vision—they play a critical role in maintaining your overall health. As we’ve discussed, an eye exam can sometimes detect signs of a brain tumor or other serious conditions. By catching these issues early, you can take proactive steps to address them before they worsen.
In addition to detecting potential health problems, regular eye exams can help monitor existing conditions, such as glaucoma or cataracts. Early detection and treatment of these eye diseases can prevent vision loss and improve quality of life. For children, regular eye exams are essential for ensuring proper visual development and academic performance.
How Can You Prepare for an Eye Exam?
If you’re scheduled for an eye exam, there are a few things you can do to prepare. First, make a list of any symptoms or concerns you’ve been experiencing, such as vision changes, headaches, or eye pain. This information will help your optometrist conduct a thorough evaluation and determine whether further testing is needed.
It’s also a good idea to bring a list of any medications or supplements you’re taking, as well as your family medical history. Certain conditions, such as diabetes or glaucoma, can run in families, so this information is valuable for assessing your risk. Finally, don’t hesitate to ask questions during your exam. Understanding the results and any recommendations will empower you to take charge of your eye health.
What Should You Do If a Brain Tumor Is Suspected?
If your optometrist suspects that a brain tumor may be causing your symptoms, it’s important to seek further evaluation from a neurologist or other specialist. They will likely order imaging tests, such as an MRI or CT scan, to confirm the diagnosis and determine the best course of action. Treatment options for brain tumors vary depending on their size, location, and type, and may include surgery, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy.
While the thought of a brain tumor can be overwhelming, remember that early detection and treatment can make a significant difference. Stay proactive, follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations, and don’t hesitate to seek a second opinion if needed. Your health and well-being are worth it.
Conclusion: Can an Eye Exam Detect a Brain Tumor?
In conclusion, while an eye exam is not a direct diagnostic tool for brain tumors, it can sometimes reveal signs that prompt further investigation. Swelling of the optic nerve, vision changes, and other abnormalities detected during an eye exam may indicate increased intracranial pressure, which could be caused by a brain tumor. This highlights the importance of regular eye exams as part of a comprehensive healthcare routine.
If you’re concerned about whether an eye exam can detect a brain tumor, the best course of action is to schedule an appointment with your optometrist. They can assess your eye health, address any concerns, and refer you to a specialist if necessary. By staying informed and proactive, you can take control of your health and ensure the best possible outcomes. Remember, your eyes are more than just a window to the world—they’re also a window to your overall well-being.